How to implement Google Analytics in 3 simple steps
Knowing how to implement Google Analytics is the first step to understanding who your website visitors are and how they interact with it.
However, implementing this tool can be a complex task, so I have prepared a guide so that you can do it step by step. Before we get down to business, let's review what makes Google Analytics so special.
Why do you need Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that provides you with essential information about your website and your business. With over 56% of pages on the web using this service, it is one of the most popular tools when it comes to website measurement. This is because Analytics offers a large amount of information about the users who visit your pages.
Here are just some of the pieces of data you can get from Google Analytics:
- Amount of traffic your website receives.
- Pages from which the users of your site come.
- Individual traffic of each page
- Number of converted leads.
- Pages your leads come from.
- Demographic information of your site visitors.
- The source where your traffic is coming from, whether it's from a mobile device or a desktop computer.
As you will see, you can get a great benefit from the information provided by Google Analytics regardless of the size of your business or website. For this reason, the following steps will facilitate the implementation of the tool and its subsequent use.
Step 1: Implement Google Tag Manager
The Google Tag Manager, also known as Tag Manager, is a free system that collects all the information from your website and sends it to other platforms such as Facebook Analytics or Google Analytics.
It also allows you to update and add tags to your Google Analytics code without having to manually type it into your site's backend, saving you a lot of time and headaches.
For example, let's say you want to know how many users clicked on the link for a downloadable PDF file. Without Google's tag manager you will have to manually change all the download links, while with this tool, you just have to add a new tag to track the downloads.
To start you must create an account in the Google Tag Manager home page.

Enter the account name and then continue.
Followed this, set up a container, which is essentially a field that contains all the "macros, rules, and tags" for your website.

Give this container a name that describes it and select the type of content to which it is associated (Web, iOS, Android or AMP).
Once this is done, click on create, review the terms of service and accept them. This action will give you the snippet of the container installation code.

This is the code snippet that you need to paste into your site's backend in order for you to manage your tags. To do this, copy and paste the two code snippets on each page of your site. According to the installation instructions of the tag manager, you need the first one in the header and the second after the opening of the body.
If you use WordPress, you can easily do this by pasting the two pieces of code into your page theme.
Tip: You can make this process even easier by installing and activating the plugin Insert headers and footers for WordPress (or its equivalent for other types of websites). This allows you to add any code to the header and footer throughout your website, where you only need to copy and paste it once.

Step 2: Create a Google Analytics account
As in the tag manager you must create an account from Google Analytics.
Enter your account and name of your website as well as the URL, specifying the category of the industry to which it belongs, as well as the time zone in which you want to obtain reports.

Once you have done this, agree to the terms of service in order to obtain your Tracking ID.
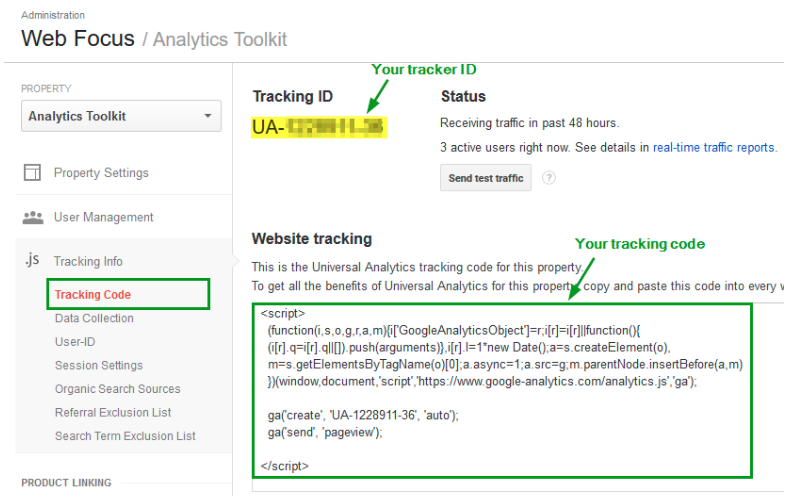
The tracking ID is a series of numbers that requests the analysis data from Google Analytics. The number looks like this: UA-000000-1. The first set of numbers (000000) is your personal account number and the second set (1) is the property number associated with your account.
This number is unique to your website and your personal data so you should avoid sharing it or making it public in any way.
Step 3: Configure the Analytics Tag with Google Tag Manager
In this step, you must configure specific Google Analytics tracking tags for your website. For this you must access the google tag manager where can you add a new label button.
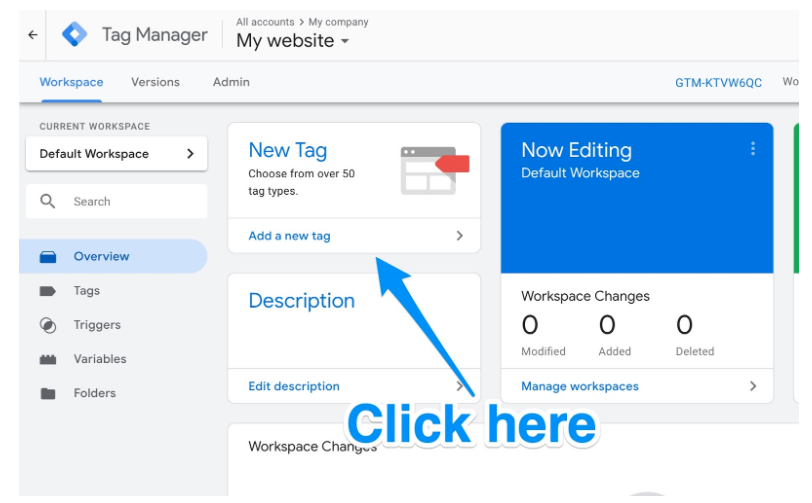
From there you will be taken to a page where you can create a new tag for your site and customize two areas of your tags:
- Configuration: Where the data collected by the label goes.
- Activator or triggering: Where you can define what type of data you want to collect.

Click on the button label configuration and choose what type of label you want to create.
In this step it will be ideal that you choose the option of "universal Anaytics" so that you can create a label for Google Analytics.
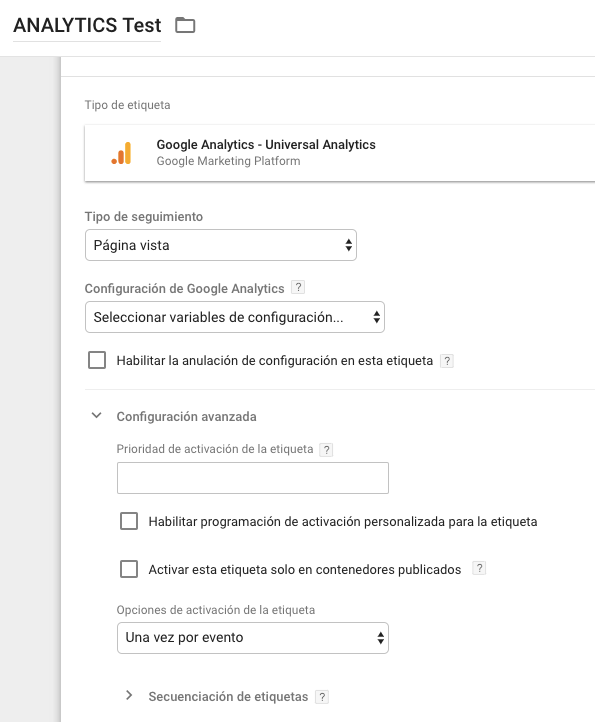
Now you can choose the type of data you want to track. Once this is done, go to the "Google Analytics Settings" and choose "New variable" which can be found within the drop-down menu.

You will then be taken to a new window where you can enter your Google Analytics tracking ID. This will send your website data directly to Google Analytics, where you can view it later.

Having done this, go to the "Trigger" button to be redirected to the "choose" section.

When everything is done, your new tag settings should look like this:

Click "Save" and with this you now have a new Google tag record and your website data will be sent directly to your Google Analytics page.
I hope these steps will help you to configure Google Analytics, but more important than configuring it, is that you can access the large amount of information that this tool provides you and you can take advantage of it.